Rate Limiting in Node.js Express with Redis
Learn how to implement robust rate limiting in Node.js Express apps using Redis, covering multiple algorithms with examples.
Tech Stack
- Node.js
- Express.js
- Redis
Featured
- Multiple rate limiting algorithms explained
- Token Bucket, Fixed Window, Sliding Window, Leaky Bucket, and Sliding Log
- Redis integration for storing rate limiting data
- Middleware implementation with examples
- Protection against brute-force and DoS attacks
Introduction
Rate limiting is a crucial aspect of web application security and performance management. It helps prevent abuse, protect against denial-of-service attacks, and ensure fair usage of server resources. By enforcing rate limits, you maintain a balance between serving legitimate users and defending against malicious activities.
Choosing the Right Algorithm
1. Token Bucket Algorithm
Overview:
- Adds tokens to a bucket at a fixed rate.
- Each request consumes a token.
- Allows short bursts of traffic up to the bucket’s capacity.
- Requests with no tokens available are delayed or rejected.
Steps to Implement:
- Create a bucket with a fixed capacity.
- Refill the bucket at a constant rate.
- For each request:
- If tokens are available → consume one and allow the request.
- If no tokens → delay or reject the request.
2. Fixed Window Algorithm
Overview:
- Divides time into fixed intervals (e.g., 1 second, 1 minute).
- Resets the request counter at the end of each interval.
- Simple to implement but can allow bursts near window boundaries.
Steps to Implement:
- Set a fixed time window.
- Maintain a counter for requests in the current window.
- For each request:
- Increment the counter.
- If the counter exceeds the limit → delay or reject the request.
- Reset the counter when the window ends.
3. Sliding Window Algorithm
Overview:
- Tracks requests in a moving time window.
- Provides smoother rate limiting compared to fixed window.
- Better reflects actual recent traffic patterns.
Steps to Implement:
- Define the window size (e.g., last 60 seconds).
- Track requests within the current window.
- For each request:
- Remove any requests outside the window.
- If count exceeds limit → reject or delay.
4. Leaky Bucket Algorithm
Overview:
- Processes requests at a constant, steady rate.
- Allows bursts up to bucket size but drains at a fixed pace.
- Excess requests are queued or dropped.
Steps to Implement:
- Create a bucket with fixed capacity and outflow rate.
- For each request:
- If bucket not full → add request.
- If bucket full → delay or reject.
- Process requests at a steady rate regardless of arrival speed.
5. Sliding Log Algorithm
Overview:
- Keeps a log (timestamps) of incoming requests.
- Works well for irregular traffic patterns.
- More accurate but requires more storage.
Steps to Implement:
- Store timestamp of each incoming request.
- Remove timestamps older than the window size.
- If the log size exceeds the limit → reject or delay the request.
Implementation with Redis
Prerequisites
- Redis server installed
- Node.js environment ready
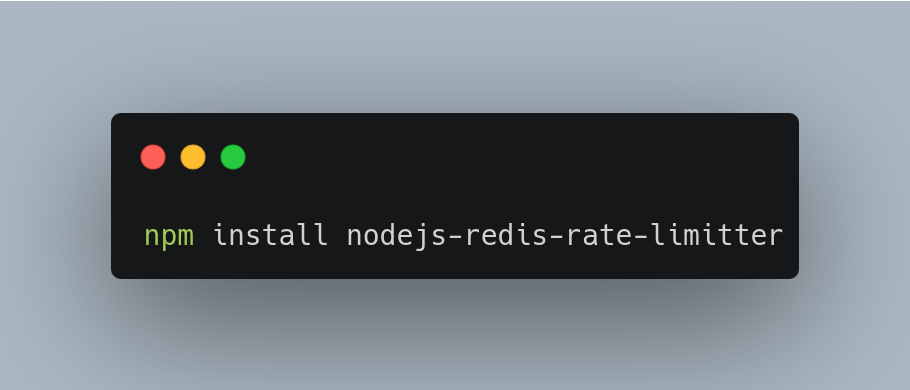
First, install the necessary packages via npm
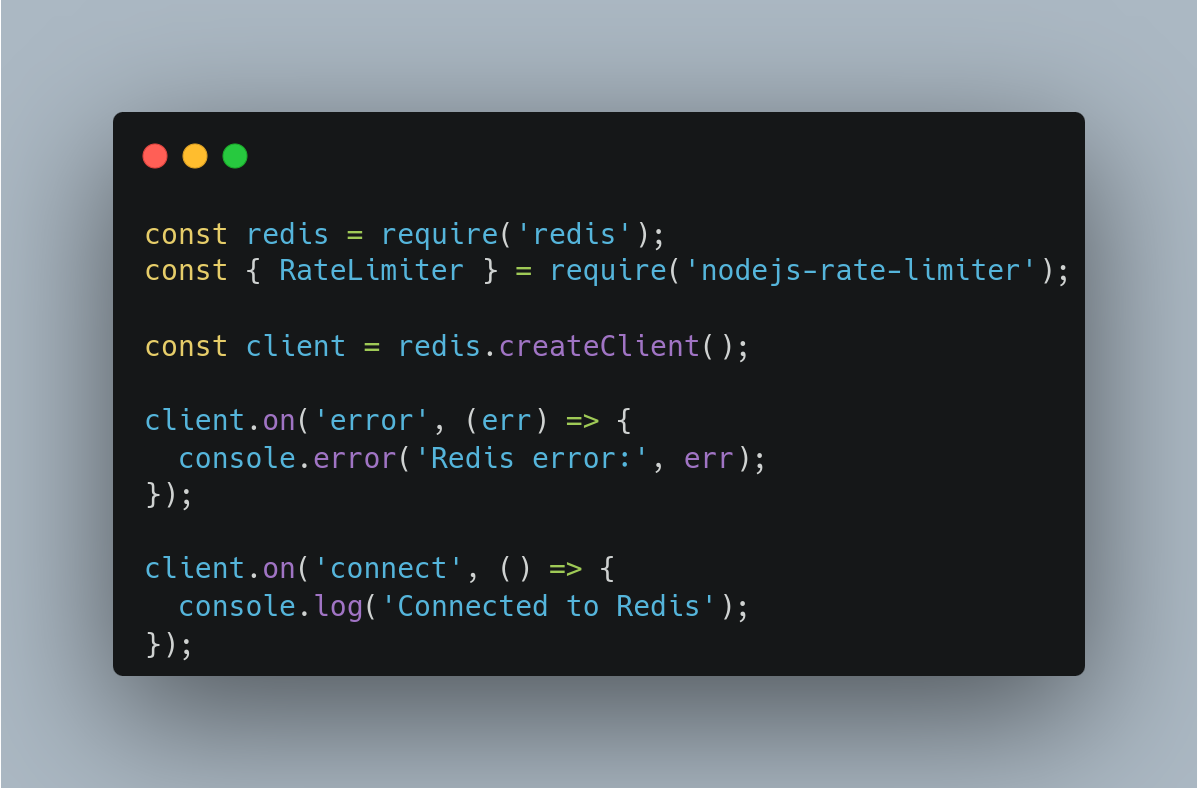
Setting up Redis Client
Example using redis library:
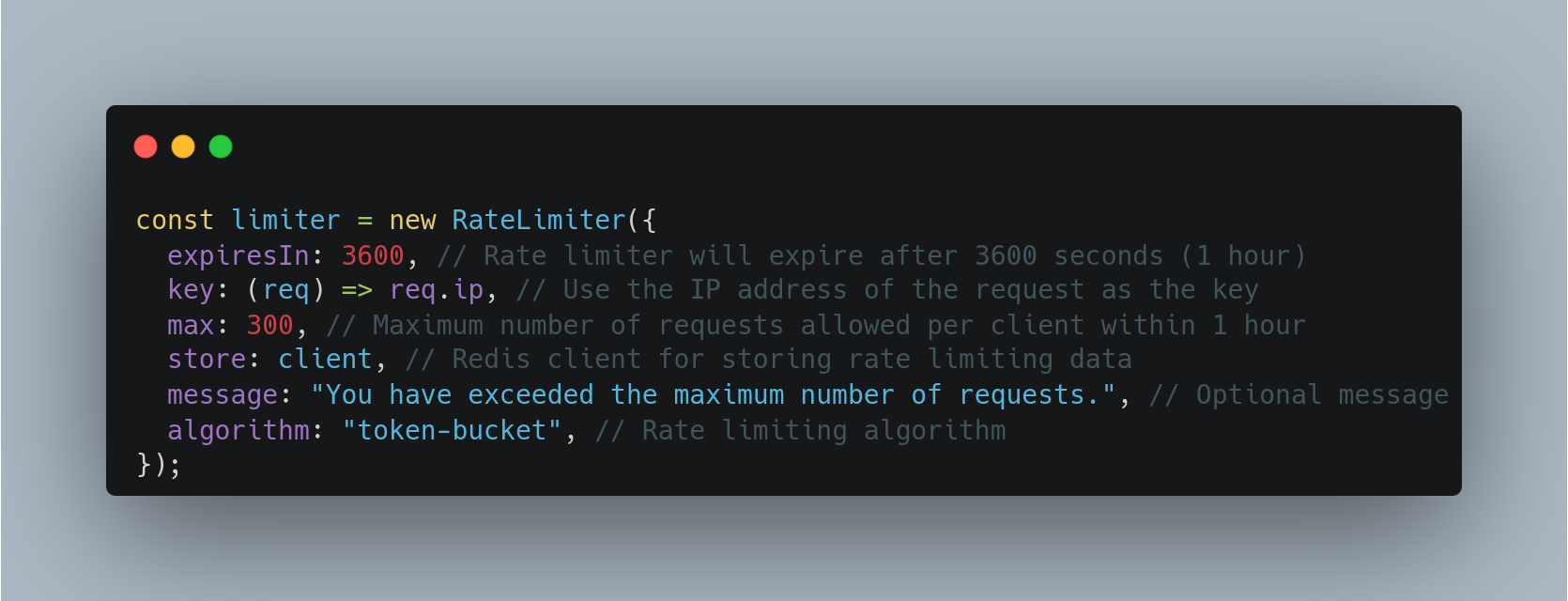
Creating Middleware
Example with Token Bucket:
Applying Middleware
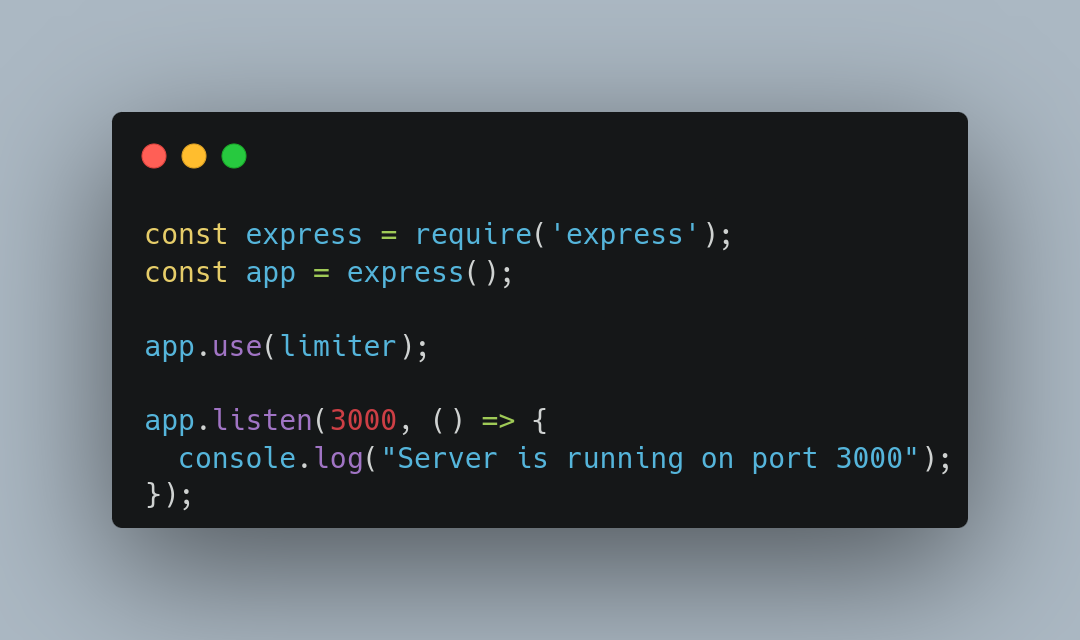
Full Code Example
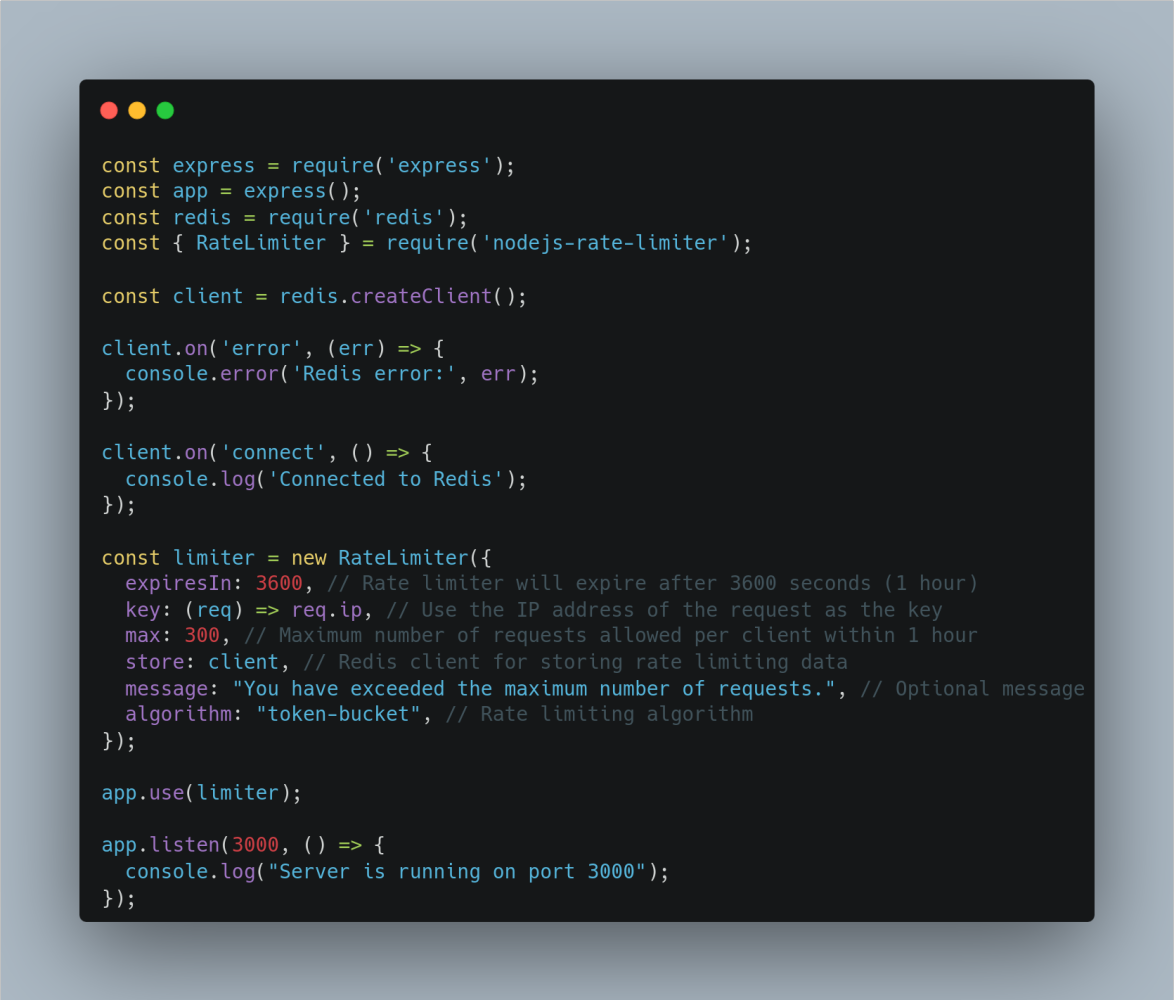
Conclusion
Implementing rate limiting in Express with Redis is essential for securing APIs and ensuring fair usage. By selecting the right algorithm and tuning parameters, you can protect your server from abuse while maintaining good user experience. Redis provides a fast and reliable storage layer for rate limiting data.
Experiment with different algorithms to find the one best suited for your application’s traffic patterns.